As Bluetooth Low Energy (LE) has evolved to version 5.2 and beyond, one of the most significant advancements has been in position tracking – a technology that is used indoors to track movements and positions of assets.
Bluetooth direction-finding methods, including both connection-less and connection-oriented modes, offer versatility that allows them to be used in a wide variety of applications. This adaptability opens new possibilities in wireless communication and location services, promising exciting advancements in the future.
One of the primary markets for this technology is in the retail sector where large stores seek to understand better how customers move around the store so that they can maximize sales potential.
Beyond retail, asset tracking can also have a profound impact on industrial efficiency. It can be deployed to monitor material handling vehicles, reducing wasted time and improving efficiency. It can also be used to drive complex digital twins allowing for the accurate replication of movements in a virtual environment.
Asset tracking is not solely focused on improving efficiency; it also plays a significant role in ensuring safety. In warehouses and distribution centers, the use of tracking tags enables a safe coexistence of employees and industrial robotics, eliminating the possibility of collisions by allowing robots to track employee movements.
Basic System Design Principles
To establish a position detection system, an array of antennas is placed in a building, whether that be a retail store, warehouse, hospital, airport, or other type of building. This array allows for highly accurate position measurement.
The methodology used can be either Angle of Arrival (AoA) or Angle of Departure (AoD). While both use the same radio frequency (RF) signal measurements, the signal processing and antenna configuration is different in each case.
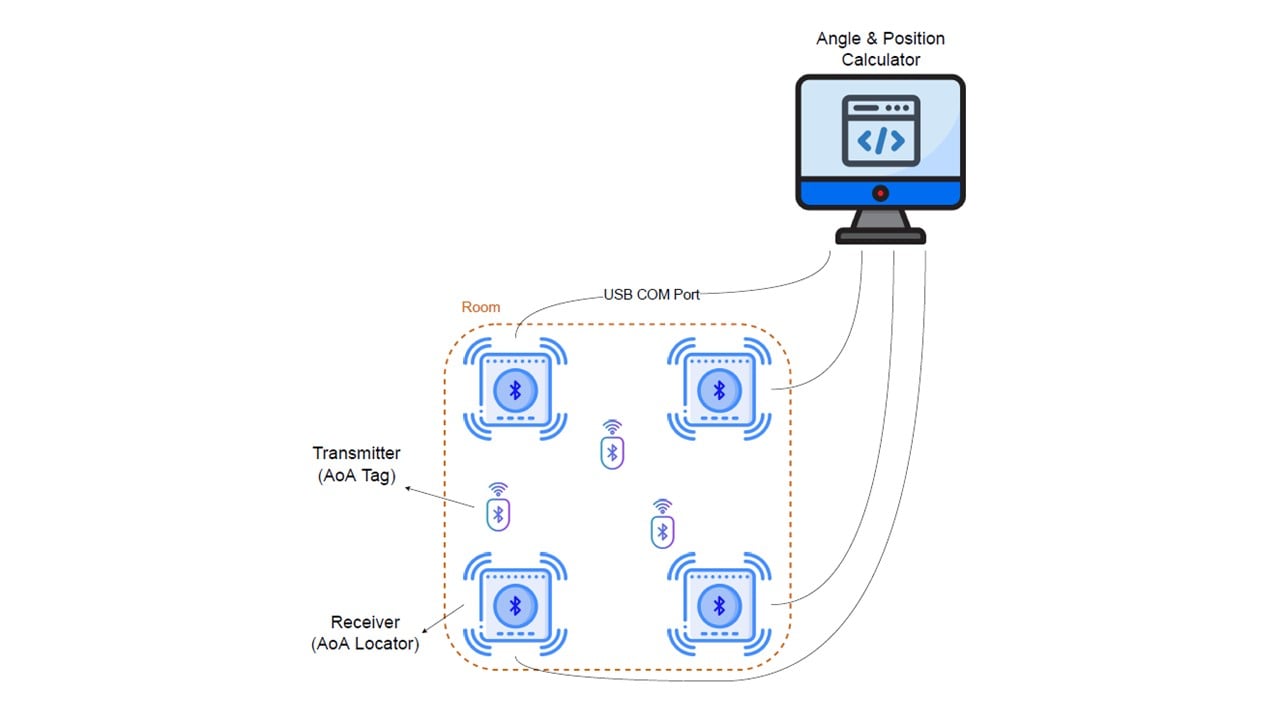
Typically, a system will consist of three main elements, a Bluetooth transmitter (AoA tag), a receiver/antenna array (AoA locator), and a system for calculating angle and position. To operate, the AoA tag sends a constant tone extension (CTE) signal.
This CTE signal spreads out in an expanding spherical pattern and is picked up by the antennas. As the wavelength/frequency of the signal is known, as is the distance between the receivers, then relatively simple trigonometry can be used to calculate the angle of the signal and, therefore, the transmitter based upon the phase difference of the signal arriving at each antenna.
Alternative Methods and Enhanced Accuracy
By performing the detection twice with two pairs of antennas, it is possible to triangulate the exact position of the AoA tag with a high degree of precision.
An alternative method that does not require angle measurement is trilateration. This is based upon a time-of-flight (ToF) distance measurement using Bluetooth 5.4 channel sounding (CS) feature or ultra-wideband (UWB).
CS is also known as high accuracy distance measurement (HADM) and many consider it to be a very accurate alternative to RSSI-based distance measurement.
onsemi’s RSL15 AoA Solution
The RSL15 from onsemi is a Bluetooth 5.2 certified secure wireless microcontroller that is optimized for ultra-low power applications including industrial, medical and AoA. The device is based around an Arm® Cortex®-M33 processor running at up to 48 MHz and features encrypted security. Providing the industry’s lowest power consumption, the peak current when transmitting is just 4.3 mA and this reduces to 36 nA in sleep mode while waiting for a GPIO wakeup. It is designed to meet the demands of a wide range of tracking applications ranging from retail and clinical settings to manufacturing and distribution centers.
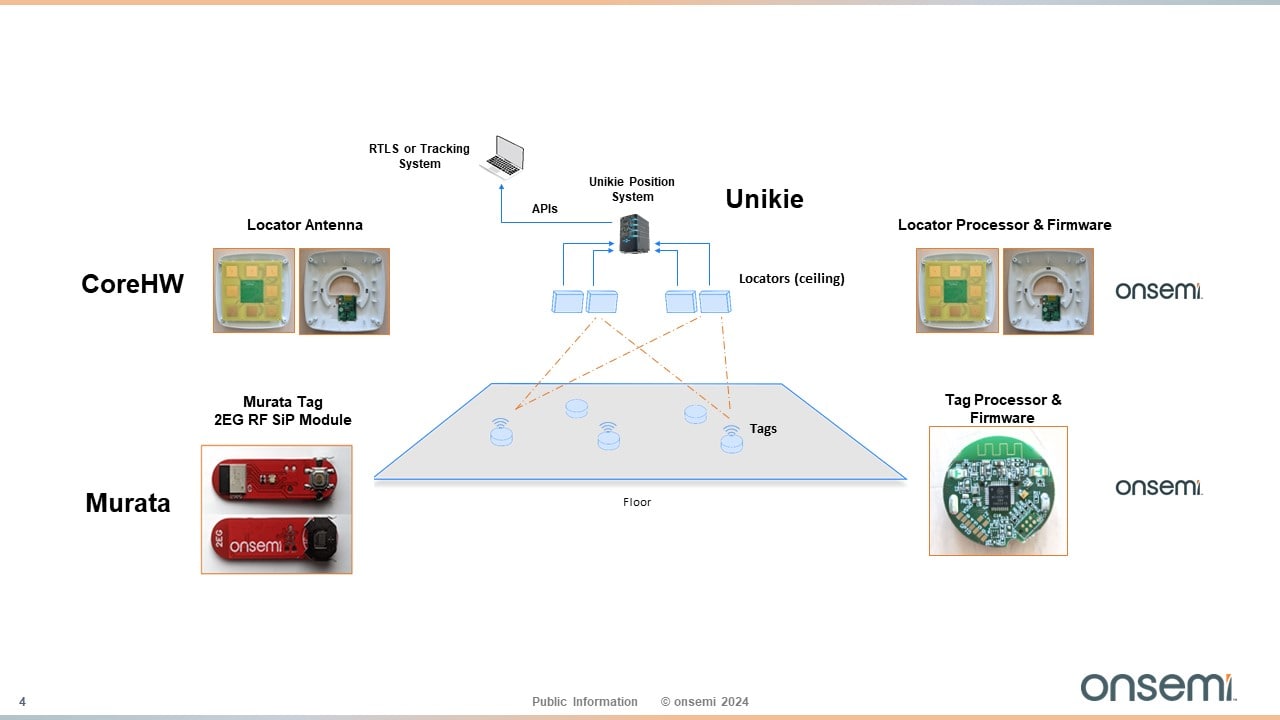
onsemi’s AoA solution utilizes the RSL15 in both the advertiser (AoA tag) and scanner/locator. This can be implemented using the RSL15 and onsemi’s software development kit (SDK) or, for a more integrated solution, Murata’s 2EG RF SIP module which integrates the RSL15.
Within the system, the advertiser generates the CTE signals which are received by the scanner. The resulting IQ samples are sent to an application running locally on a PC, or in the cloud, to calculate the angle between the scanner and the tag. These angles are then converted into Cartesian coordinates and mapped into two or three dimensions.
Sample code for both applications is available free of charge from onsemi’s website, along with a power estimator tool that allows communications protocols to be selected based upon battery lifetime.
Other onsemi partners involved in the project are CoreHW and Unikie. CoreHW supplies antenna array boards with up to 16 single-ended antenna ports. There is an AoA / AoD switch for antenna selection and connectivity for RF and digital control signals.
Unikie provides a Bluetooth Low Energy eocalization engine that is designed for real-time tracking of tags. The engine allows data to be processed either on edge servers or in the cloud, providing both flexibility and cost-effectiveness (Figure 4).
APIs facilitate seamless integration with enterprise systems, giving access to sophisticated data modeling. This enables a deeper understanding of material flows, utilization rates and behavioral patterns, marking a notable progression in location-based services and asset management.
Summary
For Bluetooth LE direction-finding to be successfully embraced, it is crucial that solutions are long-lasting and affordable. With the industry’s lowest power secure Bluetooth LE MCU, onsemi technology is at the forefront of enabling AoA future innovations.
Download our whitepaper to learn about designing the industry’s lowest-power wireless location-finding systems.